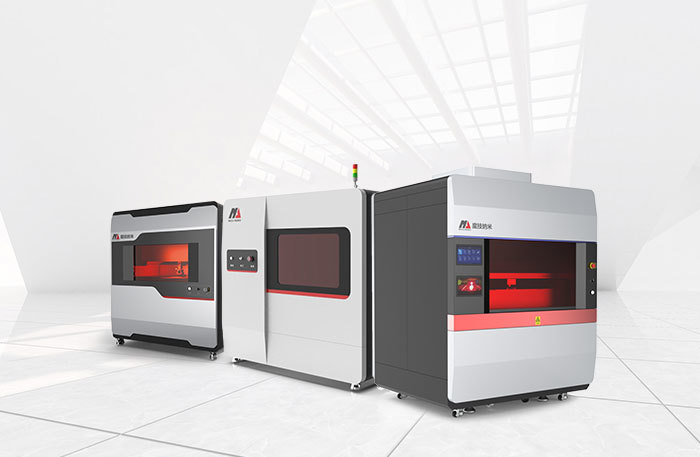
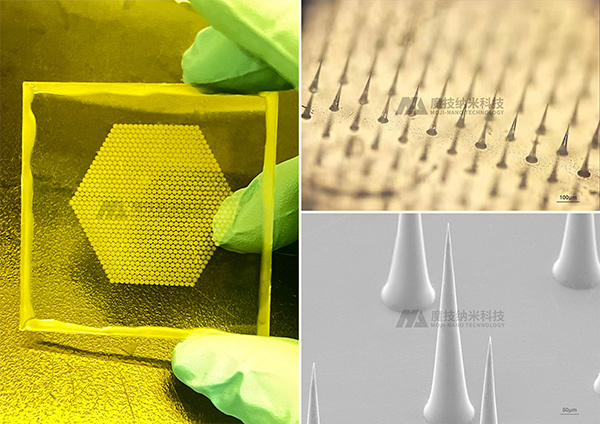
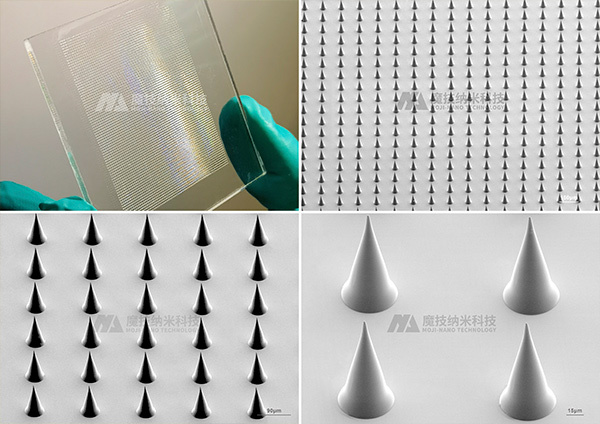
➤ Painless epidermal injection with nanoneedles
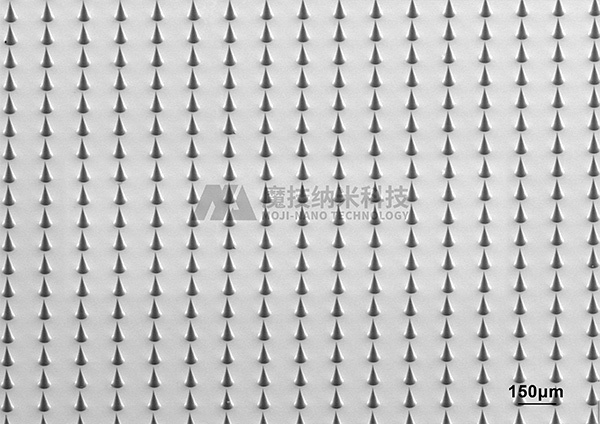
Nanoneedles fabricated by nanoscale three-dimensional technology can be used for blood collection and epidermal injection of nucleic acid-based and protein-based agents, overcoming the digestion of proteins by oral agents. Transdermal drug delivery via nanoneedles can penetrate the stratum corneum barrier and effectively deliver drugs to the intended skin layers. Compared with traditional oral administration, topical application, injection, and transdermal patches, it can simultaneously achieve efficient drug delivery and improve drug absorption rates.
Currently, MOJI-NANO technology has successfully independently developed a high-precision mass template preparation process, which enables the large-scale production of nanoneedle molds of different sizes. These molds are applied in the following areas: insulin nanoneedle patches, vaccine nanoneedles, nanoneedle contact lenses, and nanoneedles for aesthetic medical stem cell exosomes (MSC-exo). The products have the advantages of accurate drug delivery, painless and minimally invasive application, high stability, and safety.


➤ Cell growth-controlling scaffolds

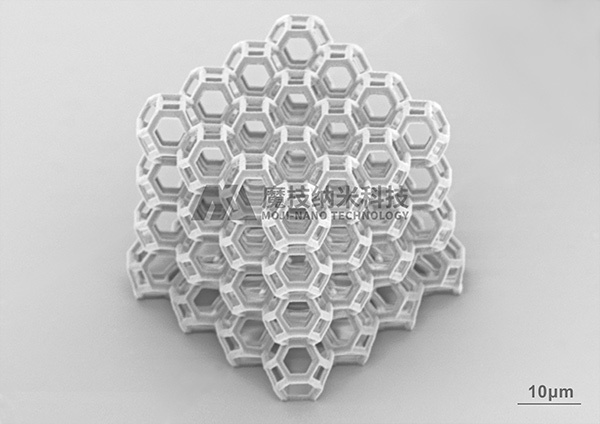


The nano 3D laser direct writing technology can fabricate various types of cell scaffolds suitable for cell growth. Through a two-step printing method, the integration of both cell-friendly and cell-repellent materials on the same scaffold can be achieved, thereby enabling the control of cell growth in three dimensions.
➤ Nanorobots for targeted drug delivery
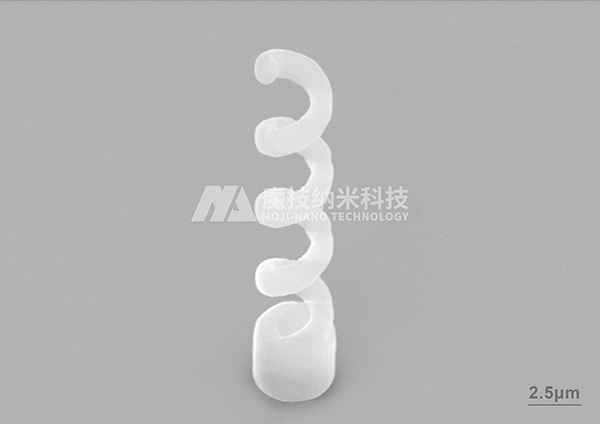
Nano 3D manufacturing can produce micro-nanorobots with high paramagnetism. By utilizing the control of an external magnetic field, it can achieve the indirect loading, targeted transport, and site-specific release of drugs in a liquid environment. Currently, in cooperation with Peking University Hospital and Beihang University, nano screw propellers are being produced.




➤ Micro drug injection
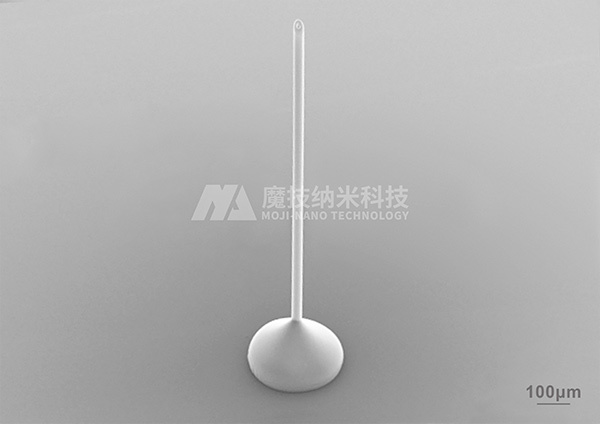




The micro hollow needles fabricated by nano three-dimensional manufacturing and printing technology can be manually controlled in six degrees of freedom using optical pressure, enabling precise loading and release of drugs.
Address
No. 1 Rongchang Road, Huangbohai District, Yantai City, Shandong Province, China
Subscribe
Get the latest information from Moji Nano Technology
Scan WeChat QR Code to Contact Us